Solar storms under the watchful eye of scientists
 Photo: Fotolia
Photo: Fotolia
Solar storms involve ejecting huge amounts of energy and matter into space. This can have disastrous consequences for earth electronics and telecommunications. The knowledge about the processes taking place on the Sun is expected to be broadened by the ESA mission, in which Polish researchers participate.
"Strong solar storms, which are actually powerful explosions on the surface of our star, involve ejecting huge amounts of energy and matter into space. Part of the charged particles ejected into space reaches the Earth and causes so-called magnetic storms on our planet" - explained the CEO of Polish company Creotech Instruments SA Dr. Grzegorz Brona, quoted in a release sent to PAP.
He explained that these storms, depending on their strength, may damage telecommunications satellites, disrupt radio transmissions in the Earth\'s atmosphere and even cause damage to energy infrastructure. "Such phenomena have accompanied us for centuries, but with the development of technology, their destructive potential grows with the increasing dependence of our civilization on electronic systems and electronic communication" - added Brona.
As the experts reminded in the release, the largest magnetic storm in modern history occurred in 1859. On September 1, English astronomer Richard Christopher Carrington observed a strong flare on the surface of the Sun, which led to the ejection of a massive amount of mass in the form of a plasma cloud at a speed much higher than the speed of the solar wind. The cloud reached Earth after 18 hours and caused a magnetic storm that caused the telegraph network breakdown all over Europe and North America.
"Scientists estimate that if the solar storm that occurred on the Sun in 1859 took place today, it would cause catastrophic damage to the telecommunications, satellite and energy infrastructure on a global scale and unprecedented material losses in trillions of dollars. According to estimates presented in the 2009 report of the US National Academy of Sciences, repairing damage would cost up to $ 2 trillion in the United States alone, which is more than 10 percent of the country\'s annual GDP" - said Dr Brona.
One of the effects of magnetic storms is the formation of large amounts of nitrates, whose traces and concentrations in subsequent years can be traced by analysing the composition of the glacial cores. Research has shown that powerful magnetic disturbances such as the one from 1859 occur on average once every 500 years. However, our present knowledge of the processes taking place in the stars does not allow us to predict when such a strong burst of plasma will happen again, whether it will reach our planet and what destruction it will cause.
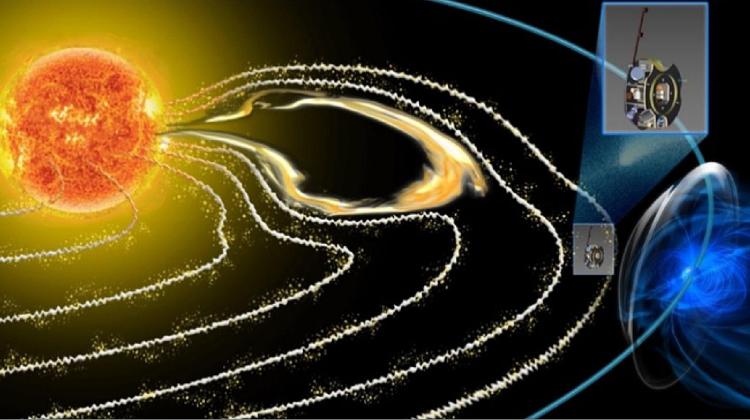
Knowledge about the phenomena occurring on the surface of the Sun is expected to be expanded by the European Space Agency mission PROBA-3.
The aim of the mission, in which Creotech Instruments SA also participates, will be studying of the outer layers of the Sun\'s atmosphere, i.e. the corona. PROBA-3 will consist of two interacting spaceships. The first will be equipped with a camera and a telescope for observing the corona. The second one, in the shape of a shield, will have to manoeuvre around the first one to cover the Sun\'s shield at the moment when the photo of the corona is being taken. Researchers believe that solar corona research will allow to learn about the interaction of the Sun\'s magnetic field with solar wind particles.
According to the representatives of the company, Creotech Instruments, on behalf of the Space Research Centre of the Polish Academy of Sciences, is responsible for the development of the coronograph driver\'s on-board computer, as well as for developing and manufacturing the controller of executive components, and designing and manufacturing ground-based testing equipment for the entire coronograph driver.
The European Space Agency mission PROBA-3 will begin in 2018 or 2019. Both components will be launched to the high orbit of the Earth. This will be the first space mission in history in which two space instruments will form a close formation and operate together in deep space conditions. The first device, equipped with a camera and a telescope, will weigh about 340 kg, the other vehicle will weigh up to 200 kg.
Currently, the process of designing key mission subsystems is being finalized. The so-called Critical Design Review is being prepared - a document that formalizes how the individual elements of the mission will be built and how the production, integration and preparation for launch of its individual elements will take place. This document concludes the 2-year mission design period. The next stage will be production.
Scientists from the American Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics presented their own idea for protecting the Earth from the plasma masses from the Sun in September 2017. They presented the idea of launching a 100,000 ton installation into space that would protect the Earth from plasma masses rushing from the Sun. "Copper coil, called a magnetic deflector, would be set at a distance of 329,000 km from our planet, and its task would be to deflect the solar wind blowing in our direction. Scientists estimate that the cost of launching the installation to space should not exceed 100 billion dollars" - reads the release sent to PAP.
PAP - Science in Poland
ekr/ agt/ kap/
tr. RL
Przed dodaniem komentarza prosimy o zapoznanie z Regulaminem forum serwisu Nauka w Polsce.